Brazil stretches all the way from the Northern Amazon basin in the state of Roraima, all the way 2,700 miles south to the State of Rio Grande do Sul, on the border with Argentina and Uruguay, and where the first Brazilian Airlines was started in 1927.
Brazil Airline industry
Brazil Airline industry has a rich history. Starting in 1927 with the foundation of Varig Airlines (Rio Grandean Airways). Founded by a German immigrant, and became Brazil’s most important Airlines for decades. For a long time, considered one of the world’s best airlines until the 1990’s.
Then, because of several reasons like: deregulation, competition, poor corporate governance, and mainly because the company was controlled by a foundation which lacked the agility necessary for the new reality of the airline business, the company has entered a period of decline, and went bankrupt in mid 2000’s.
Below you will find more information about the Airlines of Brazil, including some major old ones, and the current carriers:
LATAM Airlines Brasil
LATAM Airlines is the new airline born from the union of TAM Brasil with LAN Airlines, which was completed on June 22, 2012. Formerly TAM Airlines was Brazilian Airline brand of LATAM Airlines Group.
History of LATAM Airlines
Before coming together and forming Latin America’s largest airline, LATAM had a history full of pioneering, challenges and achievements
1929
• Commandant Arturo Merino Benítez creates LAN, Chile’s Línea Aérea Nacional.
1976
• Commandant Rolim Amaro establishes TAM, Brazil’s Transportes Aéreos Regionais.
1989
• Beginning of the privatization process. Chile’s government sells 51% of stakes to local investors and to Scandinavian Airlines System (SAS).
1990
• Brasil Central changes its name to TAM – Transportes Aéreos Meridionais.
1994
• LAN privatization reaches its peak: 98,7% of shares are acquired by the current controllers and other stakeholders.
1996
• TAM purchases Lapsa airliner from Paraguay’s government, creating TAM Mercosur.
1997
• LAN begins trading shares on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and becomes the first Latin American airline trading ADRs on this major stock exchange.
1998
• Establishment of TAM Viagens.
• Arrival of the first A330 and completion of TAM’s first international flight from Sao Paulo to Miami.
2006
• LAN launches its Premium Business category.
• TAM S.A. IPO at New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
2008
• LAN ends its short distances fleet renewal process; fleet is now formed by A320 airplanes.
• TAM launches its new logo.
• Arrival of TAM’s first Boeing 777-300ER.
2009
• LAN lauches cargo operations in Colombia and domestic passengers operations in Ecuador.
• Multiplus Fidelidade becomes an independent company.
• TAM announces the acquisition of Pantanal Linhas Aereas.
2010
• LAN buys Colombian airline Aires.
• TAM officially joins Star Alliance.
• TAM successfully performs the first flight in Latin America with biofuel from jatropha.
2011
• LAN and TAM sign tying arrangements related to the business combination between both companies.
2012
• LATAM Airlines Group is born out of the joint operations of LAN and TAM.
2014
• TAM joins oneworld® alliance. Now, all air passenger transportation LATAM Group companies are part of the same global alliance.
Financial news about LATAM
In October 2019, LATAM’s demand grew by 17.4% in the month. It accounted for 37.5% of the domestic Revenue Passenger Kilometer (RPK), representing a 13.1% change over the same period of 2018.
The company ended October 2019 with a 71.4% stake and a low of 10.6 in RPK.
Its third quarter financial results for the year revealed operating income of $ 268.9 million during the period, a 21.8% increase over July, August and September 2018. Operating margin was 10.1%, while net revenue totaled $ 86.3 million, or $ 51.1 million higher than last year’s third quarter.
Driven by 11.1% growth in passenger revenue, the airline’s total revenue increased 6.9% year-on-year. Revenue per Available Seat-Kilometer (RASK) grew by 9.1%, as did the number of people transported, which was 7.6% higher and represented 1.4 million more passengers in Brazilian domestic operations and affiliates of the Hispanic markets.
Total operating expenses for the third quarter increased 5.5%, while Cost per Available Seat-Kilometer (CASK) increased 3.6%. According to Latam, cost increases were driven by hyperinflation in Argentina and the reversal of performance bonus provision for the third quarter of 2018. Latam Group also reduced its operating margin target to approximately 7%.
LATAM Fleet
Boeing 787-9
| Capacity | 313 passengers |
| Length | 63,00 mts |
| Wingspan | 60,00 mts |
| Maximum takeoff weight | 251,360 kg |
| Emergency exit | 8 |
| Toilet facilities | 8 |
Boeing 787-8
| Capacity | 247 passengers |
| Length | 56,72 mts |
| Wingspan | 60,13 mts |
| Maximum takeoff weight | 227,930 kg |
| Emergency exit | 8 |
| Toilet facilities | 6 |
Boeing 767-300
| Capacity | 221-238 passengers |
| Length | 54,2 mts |
| Wingspan | 47,16 mts |
| Maximum takeoff weight | 184,611 kg |
| Emergency exit | 8 |
| Toilet facilities | 7 |
Airbus 350
| Capacity | 339 passengers |
| Length | 65,23 mts |
| Wingspan | 64,75 mts |
| Maximum takeoff weight | 268,9 kg |
| Emergency exit | 8 |
| Toilet facilities | 8 |
Airbus 321
| Capacity | 220 passengers |
| Length | 44,51 mts |
| Wingspan | 35,8 mts |
| Maximum takeoff weight | 89,000 kg |
| Emergency exit | 8 |
| Toilet facilities | 3 |
Airbus 320-200
| Capacity | 168-174 passengers |
| Length | 44,51 mts |
| Wingspan | 34,10 mts |
| Maximum takeoff weight | 77,000 kg |
| Emergency exit | 8 |
| Toilet facilities | 3 |
Airbus 319
| Capacity | 144 passengers |
| Length | 33,84 mts |
| Wingspan | 34,10 mts |
| Maximum takeoff weight | 70,000 kg |
| Emergency exit | 6 |
| Toilet facilities | 3 |
Boeing 777
| Capacity | 379 passengers |
| Length | 73,08 mts |
| Wingspan | 64,80 mts |
| Maximum takeoff weight | 346,544 kg |
| Emergency exit | 10 |
| Toilet facilities | 10 |
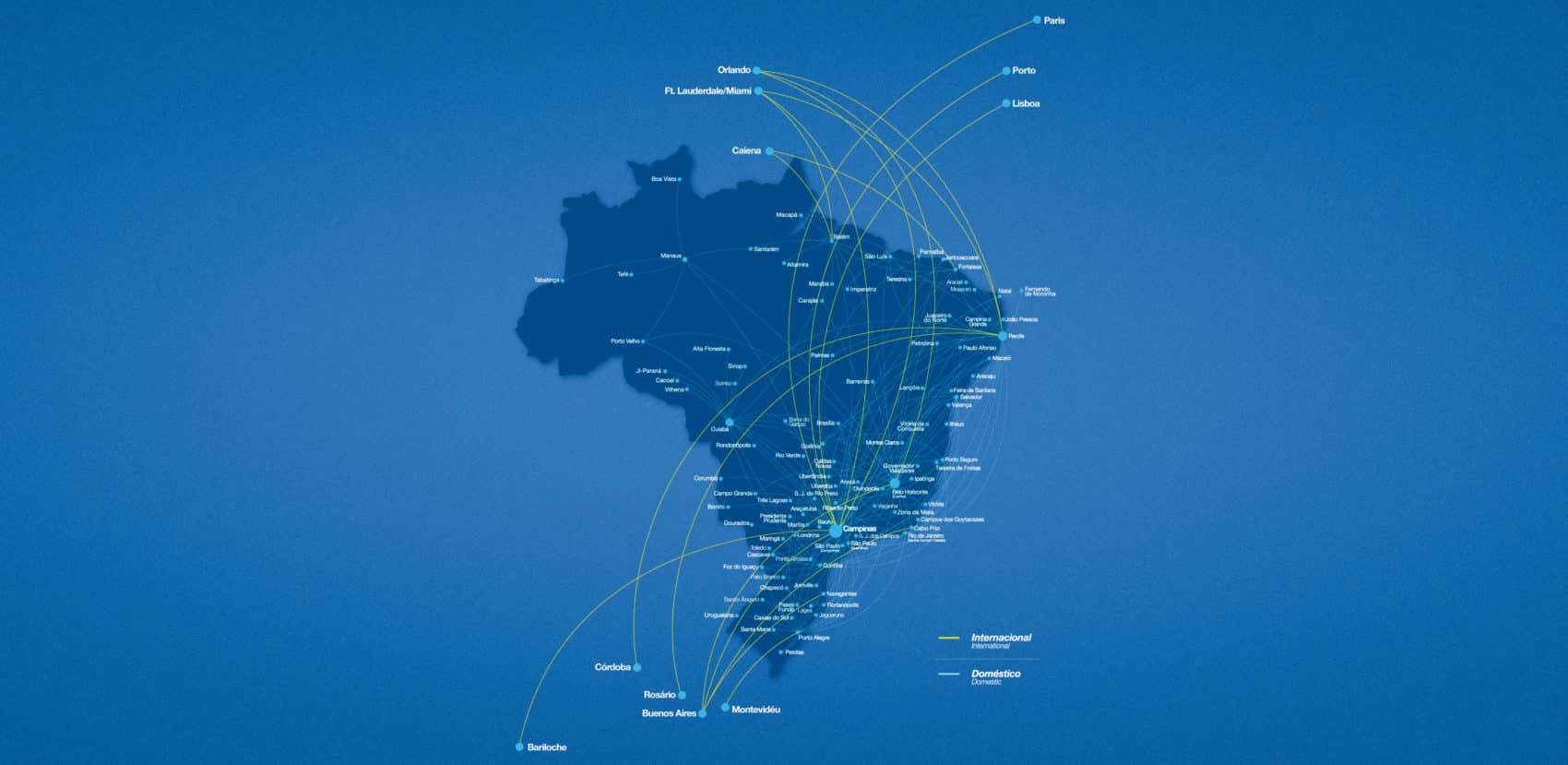
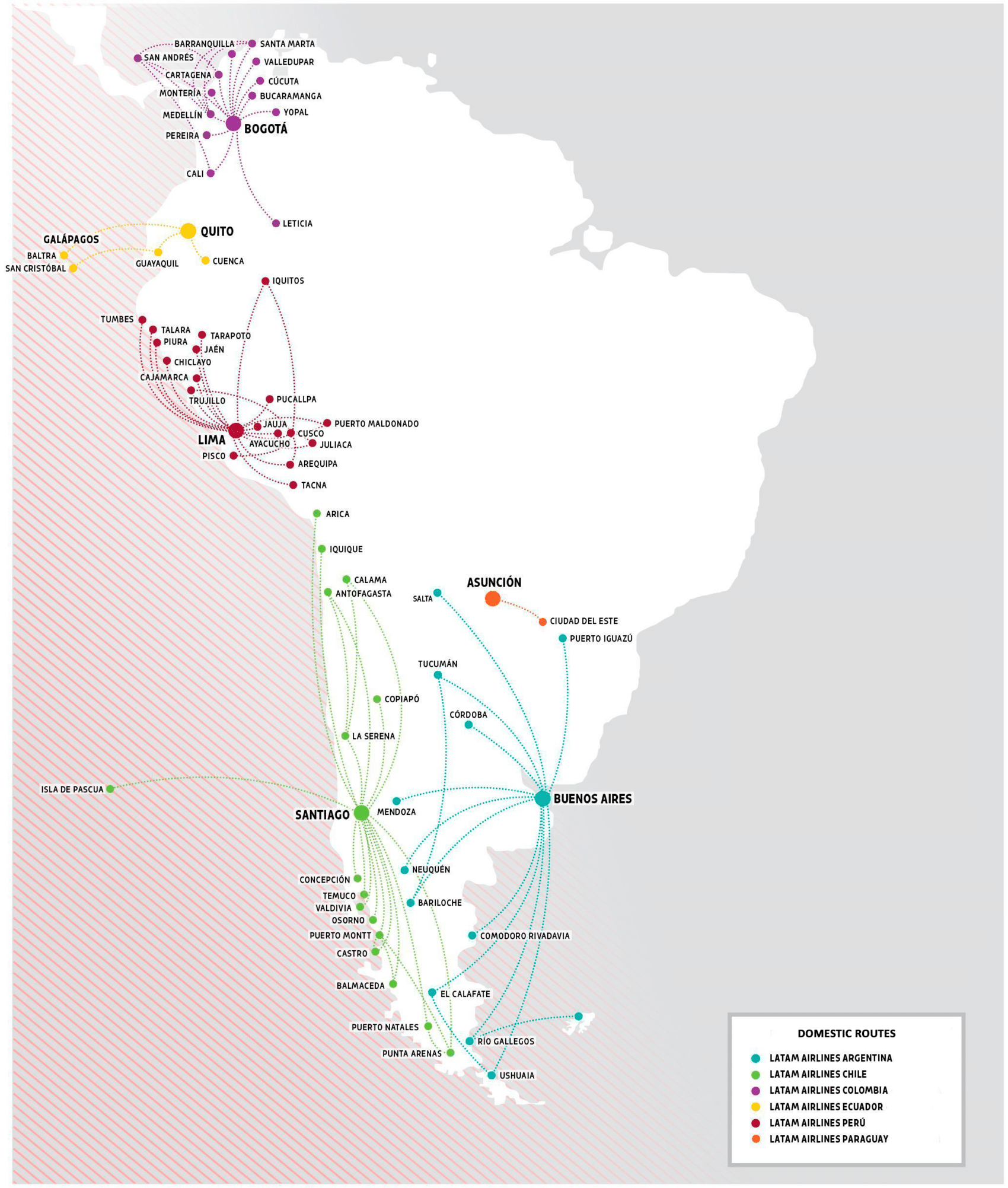
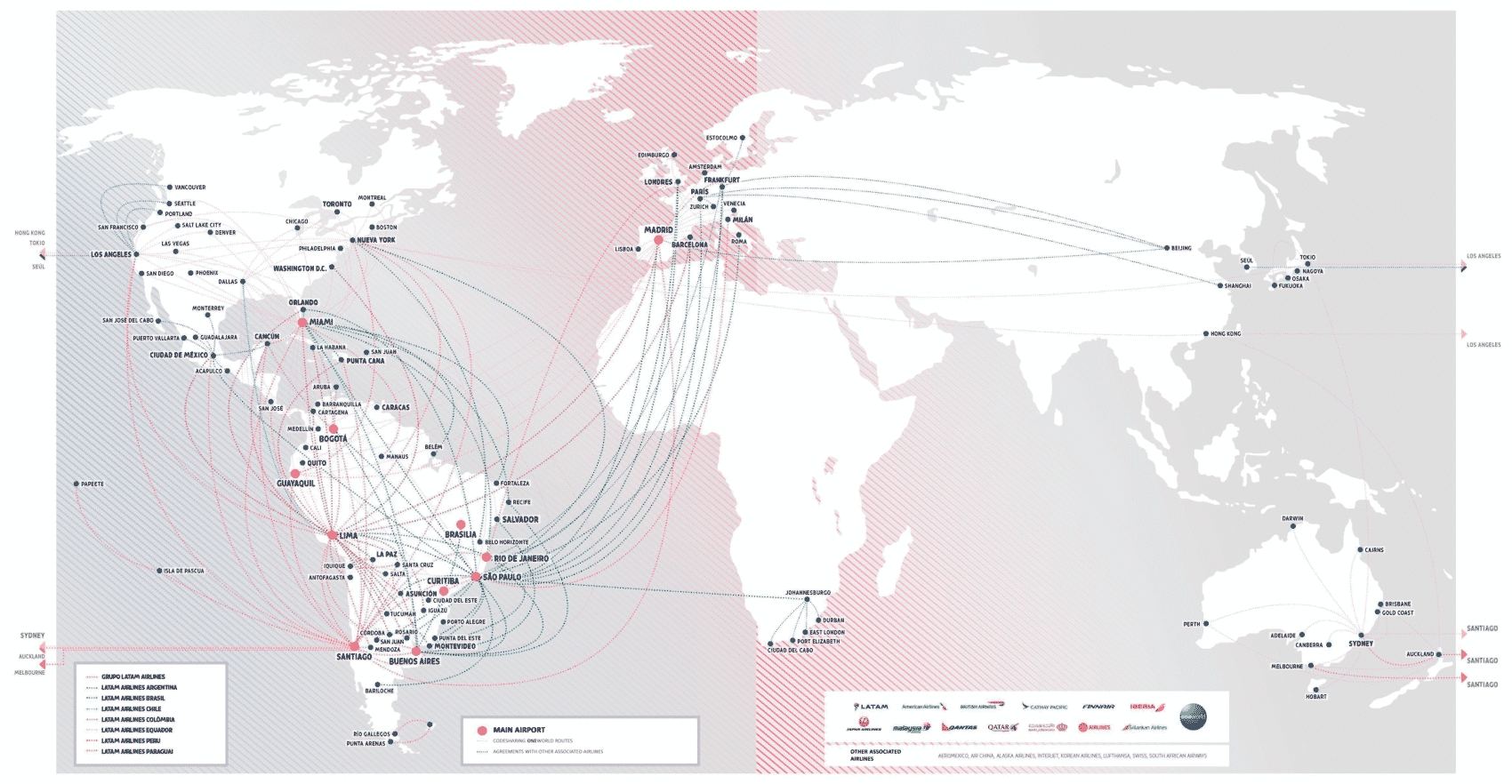
LATAM Routes
BRAZIL
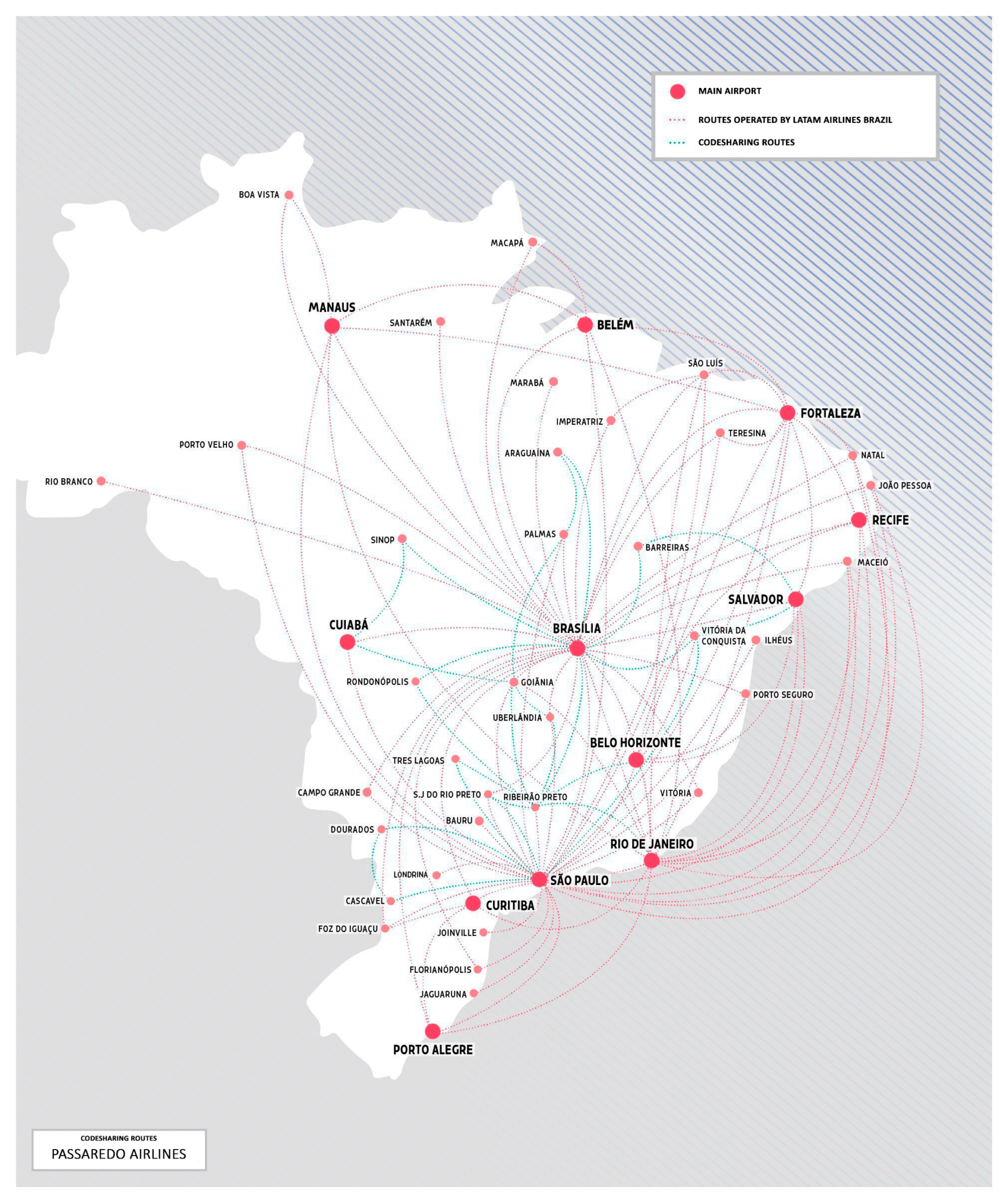
SOUTH AMERICA
WORLDWIDE
GOL Airlines Brasil
GOL have been in operation since 2001 and, today, is one of the fastest growing airlines in the world.
GOL is also the airline that serves the most passengers in Brazil, operating around 900 flights every day.
History of GOL Airlines
2001
• GOL kicks off its operations at 6:56 AM on January 15, when a Boeing 737-700 heading to the Congonhas Airport in São Paulo takes off from Brasília International Airport.
• GOL revolutionizes Brazilian commercial aviation by eliminating the traditional paper ticket and launching the reservation (locator) code. This makes traveling easier for passengers and helps ensure lower fares.
2002
• On March 17, GOL begins operating the Rio de Janeiro – São Paulo air shuttle, known as Air Bridge, it is one of the most coveted routes in the country.
• GOL receives its first Next Generation Boeing 737-800, which offers high operating efficiency, safety and comfort and is well suited to long routes.
2003
• In December, GOL launches its night flights, nicknamed “night owls”. Since their implementation, these flights been very successful, reaching an average occupancy rate of 90%.
• Launch of the web check-in service. This system allows passengers who are registered on GOL’s website and have only carry-on luggage to check in up to three hours before the flight.
2004
• GOL launched its IPO on the São Paulo Stock Exchange (Bovespa) and the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), selling over 33,050,000 preferred shares and raising R$878,138,500.00.
• With the sale of R$ 1.6 billion in tickets through its web site, GOL consolidates its position as one of the largest e-commerce companies in Brazil.
2005
• On September 16, GOL opens a new base of operations in Boa Vista, Roraima, becoming the first Brazilian airline to operate in all of Brazil’s state capitals.
• GOL acquires its first aircraft with winglets, the Next Generation Boeing 737-700, registered as PR-GOZ. The winglets technology provides better performance during takeoffs, allows for longer flights and improves fuel efficiency.
2007
• With the acquisition of Varig on March 28, GOL becomes one of the largest airlines in Latin America, transporting over 20 million passengers a year.
• On July 1, GOL signs an agreement to sell Delta Air Lines tickets, allowing for faster connections between the two airlines.]
2008
• GOL is the first Brazilian airline to offer a service that allows passengers to complete their check-in using only their mobile phone. The project was launched at Santos Dumont Airport in Rio de Janeiro.
2009
• GOL installs self-service kiosks at Brazil’s major airports. Passengers that use these kiosks don’t have to go to the check-in counters and save time.
• GOL enters agreements with American Airlines and Air France/KLM to operate codeshare flights, which also offer mileage program benefits.
2010
• GOL launches another technological innovation to make travelling even easier for its clients: the GOL iPhone App. With the new app, passengers traveling without baggage can check in on domestic flights and receive their boarding passes on their iPhone.
2011
• GOL signs a codeshare agreement with Qatar Airways, the national airline of Qatar
2014
• GOL and Air France-KLM announce a strategic partnership to expand the number of codeshare flights, providing more benefits to the passengers of both airlines.
• GOL launches another exclusive service in Brazil. With the Express Baggage service, passengers can use the self-service kiosks to check in, as well as weigh and tag their baggage.
2015
• Pet owners may now travel with their pets in the airplane cabin, provided certain requirements are met. They must be transported in pet carriers and placed under the seat.
2016
• With the goal of improving its services and offering the best flight experience to its passengers, GOL launched the Premium Class, which provides passengers with a range of exclusive benefits, from check-in to arrival. The new service is available on all international routes.
2018
•GOL announced new direct flights to Miami and Orlando departing out of Brasilia and Fortaleza. The new routes began operating on November 4. The arrival of the modern 737 MAX airplanes equipped with the latest technology have made these new international flights possible, offering a better travel experience to customers.
Financial News about GOL
In October 2019, GOL posted Revenue Passenger Kilometers (RPK) growth of 11.6%. It gained 36.7% of the domestic RPK, representing a 7.5% change compared to the same month of 2018. GOL also achieved an 11.6% share and a 30.5% increase in the RPK. .
GOL Linhas Aéreas Inteligentes recorded a record net revenue of R, 7 billion in the third quarter of 2019. The growth, compared to the same period last year, is 28%.
RPK increased by 12.8% to 11.1 billion in the same period, driven by the 13% increase in passenger volume: nearly 10 million customers in the quarter, resulting in a 38% domestic market share, according to data from the National Civil Aviation Agency (ANAC). In the corporate segment, according to data from the Brazilian Association of Corporate Travel Agencies (ABRACORP), 39% of passengers flew by GOL. There are more than 750 daily flights using a single Boeing 737 fleet. In 19 years, the company has carried 450 million passengers.
There are 76 destinations operated by the company itself (there were 67 at the beginning of the year). In total (counting reginal and international), they reach 300.
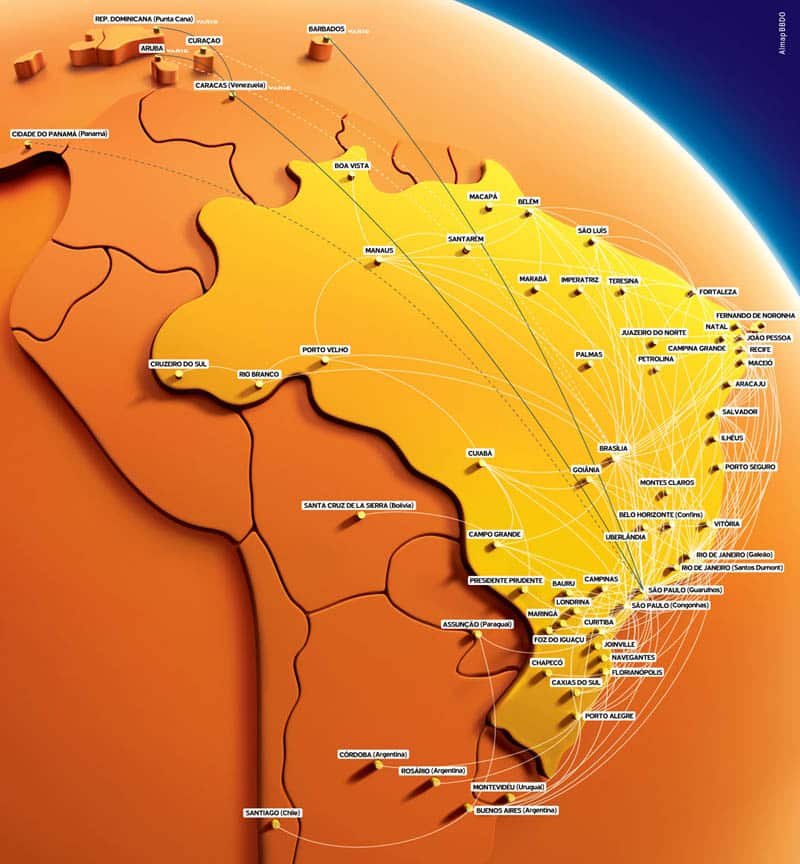
GOL Routes
GOL Airlines
PARTNER AIRLINES
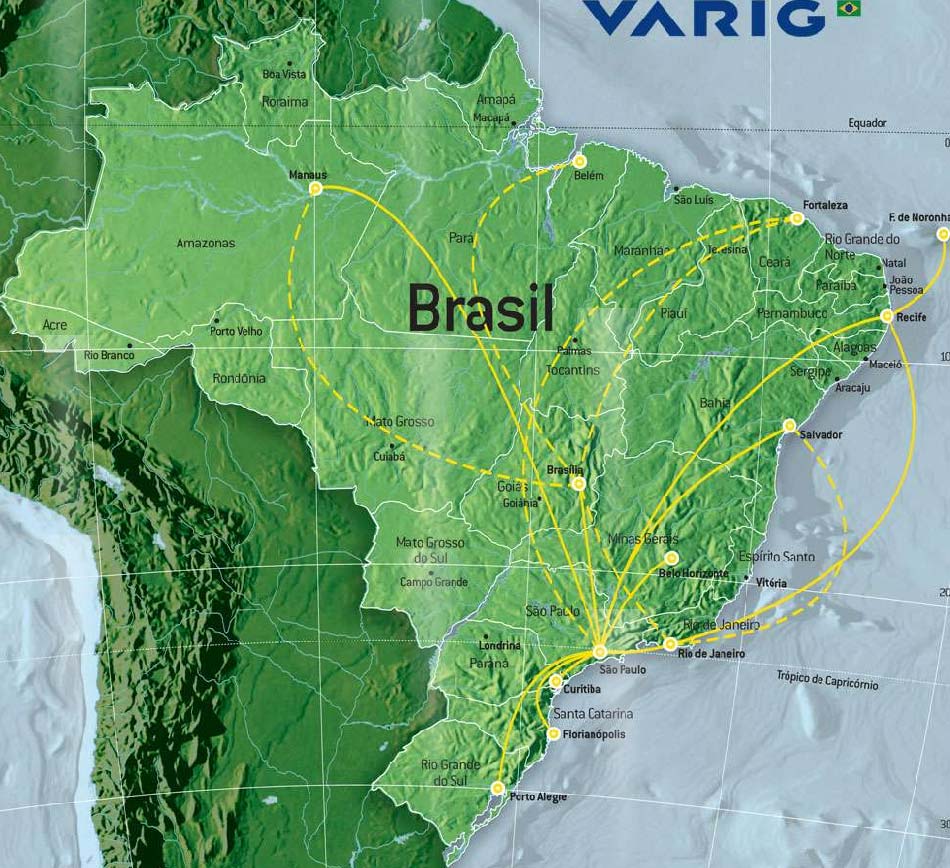
Varig Domestic Lines
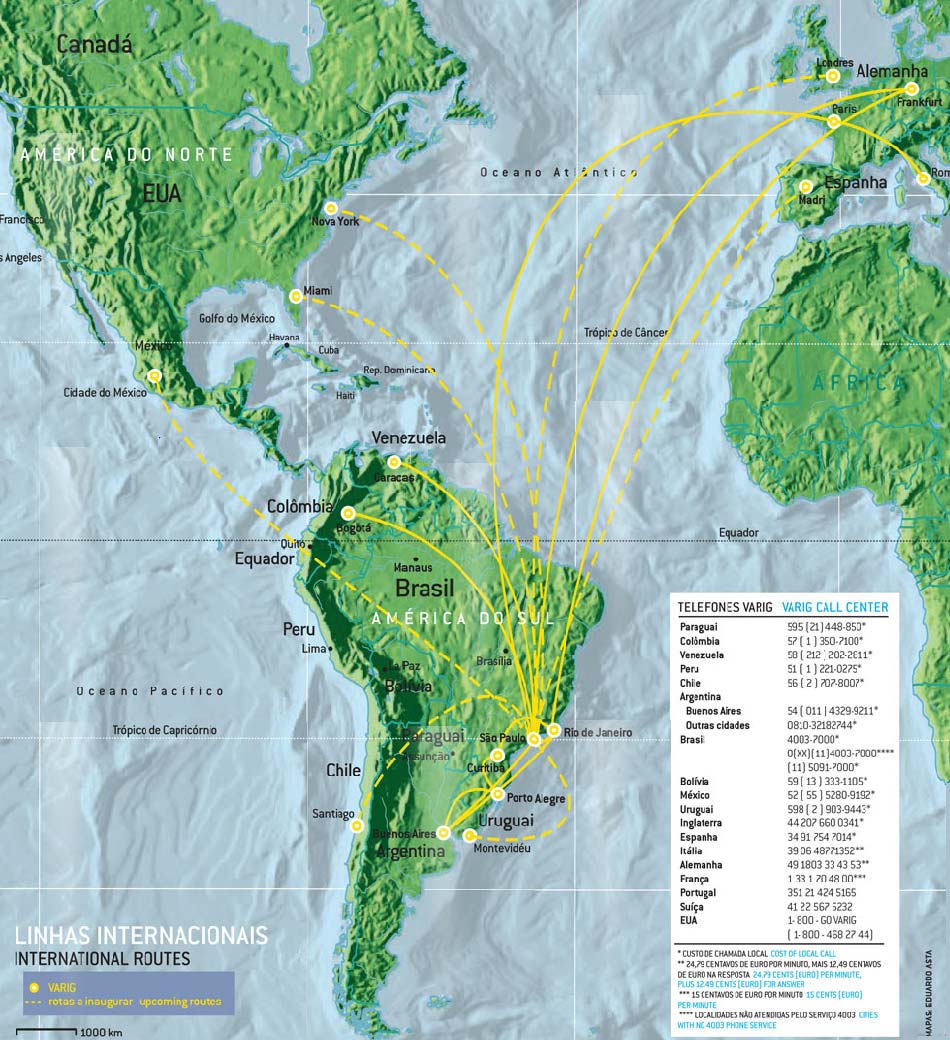
Varig International Lines
Webjet Airlines

AZUL Airlines
Since December 2008, Azul has had the largest airline network in the country in terms of cities served. Azul Airlines provides services to more than 100 destinations, and 792 daily flights. Expanded operations with selected non stop service to the United States, Europe and South America.
History of AZUL Airlines
With a 32% departure share in the Brazilian aviation market, Azul has been established as the third largest airline in the country.
A differentiated business strategy, customer experience, and innovative branding are the key drivers of the continuous growth.
Among other awards, Azul was named the third best airline in the world by TripAdvisor Travelers’ Choice in 2017, the best low cost carrier in South America for the sixth consecutive year by Skytrax in 2016, and the world’s most on-time low-cost airline in 2015 by the Official Airline Guide (OAG).
Financial News about AZUL
Azul Airlines is now one of the most profitable in the world. Azul’s income excluding interest, taxes and amortization, or EBITDA, was R$ 935.8 million, 24.4% higher, representing a margin of almost 31%. Net income, excluding the non-cash impact of exchange variation, totaled R$ 444.4 million, up 56.7% from July to September 2018.
In addition, 27.1% more passengers traveled with Azul in the period, compared with a 26.1% growth in supply, resulting in a load factor of 84.3%, 0.6 percentage points higher than in 3Q18. .
Azul’s fleet closed September with 133 aircraft. One third of this is considered new generation equipment, which represents 45% of the airline’s capacity in the quarter.
In October 2019, Azul presented a 40.1% growth in its demand in the month. It also accounted for 25.3% of domestic demand, up 35% from the same month last year.
The company achieved 17% share and 23.3% growth compared to the same period of 2018.
Azul earned R $ 3 billion in the third quarter of this year, a record net revenue for the company and growth of 25.5% compared to the third quarter of 2018. The company’s operating income increased 31.4% to R$ 559.3 million, with a margin of 18.5%.
Former Airlines
Avianca
Avianca Brasil, officially Oceanair Linhas Aéreas S/A, has filed for bankruptcy protection and lost most of its fleet on May 2019. The carrier, which is controlled by the same holding company as publicly traded Colombia-based Avianca Holdings SA, was operating around 30 flights per day using the planes it had left.
Vasp Airlines
The airline was established on 4 November 1933 by the state government of São Paulo. VASP (Viação Aérea de São Paulo) was the first airline to serve the interior of the state of São Paulo. By December 2007, the once-proud company had stopped flying altogether, and was reduced to providing maintenance services to other airlines.